Primer design and general considerations for Adapt-PCR
📄Download Page as PDF
Overview
In specific cases, the eProtein DiscoveryTM user may have the desired gene of interest (GOI) cloned into a vector backbone, or present on genomic DNA or linear templates. This protocol provides general primer design considerations to support users in converting these GOIs into eGenes compatible with the eProtein DiscoveryTM system.
Design of loci-specific primers with overhangs
Prior to using plasmid or linear DNA as template for Adapt-PCR check for the presence of 3C or TEV protease cleavage sites in the sequence of the template. The presence of these sites should be avoided as their presence may interfere with Adapt-PCR and result in a low quality product. Amino acid sequences for 3C and TEV are listed below:
- 3C: LEVLFQGP
- TEV: ENLYFQS
Design loci-specific primers to amplify your GOI from the plasmid backbone. Primer design considerations are listed below:
- The 5’ end of the forward primer should NOT include the translation start codon (ATG) (see fig 1).
- The 5’ end of the reverse primer should NOT include the translation stop codons (TAA or TAG or TGA) (see fig 1).
- The loci-specific primers can be 18-25 bp long, ideally ending with a G or C or GC at the 3’ end.
- GC range of the loci-specific primers should be within 30% to 70%, with 50% to 55% being ideal.
- The annealing temperature of the loci specific primers should be in the range of 55 to 70°C.
- The annealing temperature of the loci-specific primer pair should not be higher than the extension temperature of the HF polymerase you wish to use.
- The loci-specific primer pair should not have a melting difference >5°C.
- Avoid self-complementarity within the primers and between the primer pair.
Append the loci-specific forward and reverse primers with the following tail sequences at the 5’ end of each of the primers:
- Forward Primer 5’ tail sequence: 5’ CTCGAGGTTCTGTTCCAAGGACCT
- Reverse Primer 5’ tail sequence: 5’ GCTCTGGAAGTACAGGTTCTC
- An example of loci-specific primers appended with the tail sequences is shown in Table 1.
Place the order of the oligos using standard desalting synthesis conditions.
Once the oligos are received, reconstitute it to standard 100 μM as per the manufacturer’s guidelines using nuclease free water.
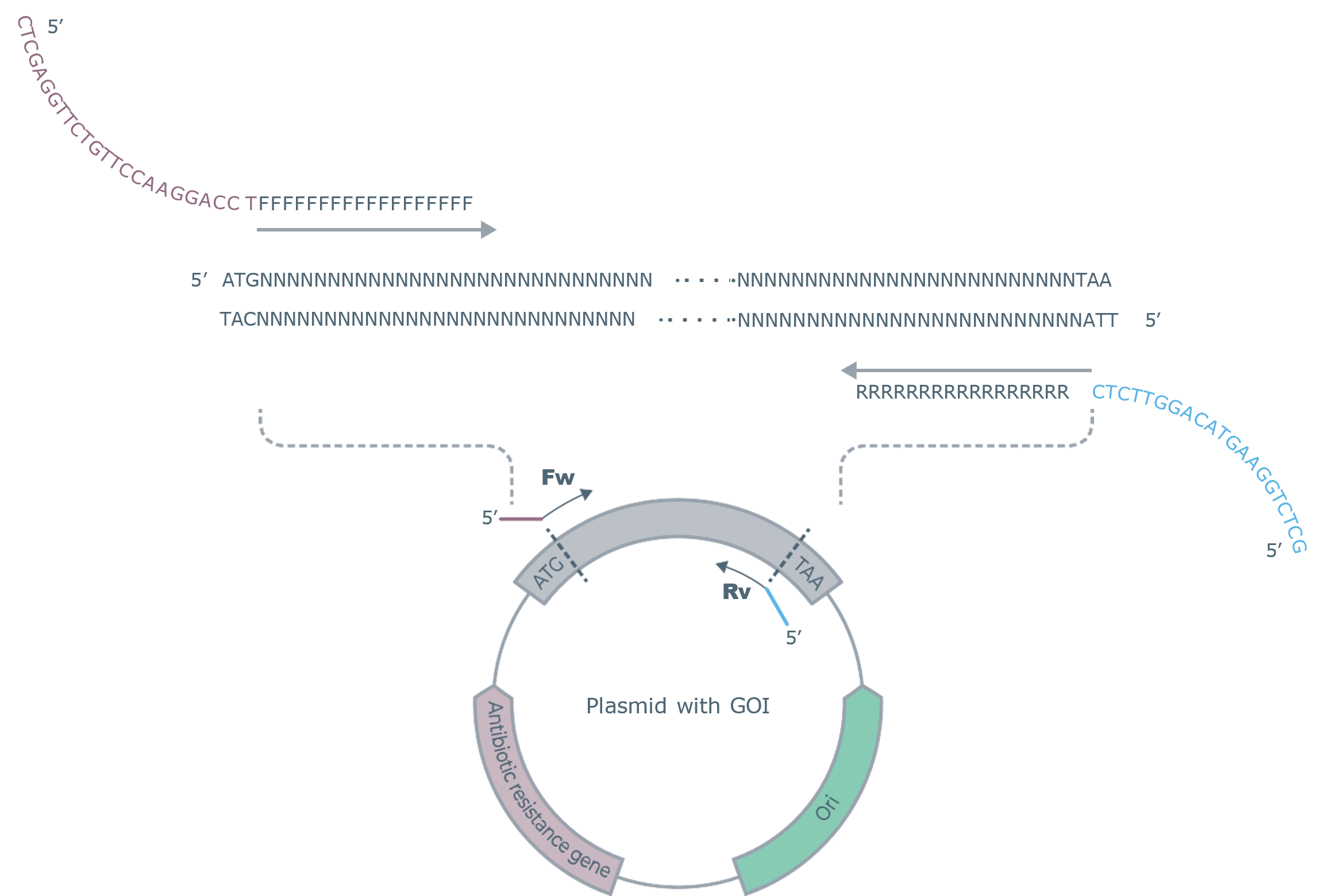 Figure 1. Illustration indicating the positions of the forward and reverse primer pair to amplify the GOI from a plasmid backbone.
Figure 1. Illustration indicating the positions of the forward and reverse primer pair to amplify the GOI from a plasmid backbone.
 Table 1: An example of Adapt-PCR primer design based on the sequence illustrated in *F & R refer to the 5’ to 3’ forward and reverse primer sequences respectively.
Table 1: An example of Adapt-PCR primer design based on the sequence illustrated in *F & R refer to the 5’ to 3’ forward and reverse primer sequences respectively.
General considerations for Adapt-PCR
Use a high fidelity PCR Mastermix. Carry out a low number of PCR cycles (up to 20 cycles).
- This step may require optimization to get a single band of the expected size. The typical yield from a single 50 μL PCR reaction is sufficient for subsequent steps. If using plasmid as the starting template, it is important to digest the template, as carried over plasmid DNA could interfere with CFPS reactions. Achieve this by adding Dpn1 enzyme directly to your PCR product prior to clean-up.
- Add 20 units of DpnI to 50 μL PCR product and incubate the reaction in a thermocycler set at 37°C for 1h.
- Prior to PCR purification, check the PCR product on an agarose gel. If you observe a single band of the expected size, proceed to purify the PCR product using any PCR cleanup method of your choice.
- Alternatively, resolve the bands on an agarose gel and proceed to excise the correct band to purify using gel extraction kit. To use the final product as template for eGene assembly application, normalize the PCR purified product to 2 nM using standard 10 mM Tris, pH 8.0 or 0.1X TE, pH 8.0.
Risks and challenges associated with this protocol
Currently our eProtein Discovery platform is designed to express proteins codon optimized for expression in E. coli. Codon usage from other sources such as humans, plants or even another genus of bacteria, with a different codon usage, may affect the total protein expression. Nuclera is unable to guarantee that an amplified construct will express. To gain maximum advantage of the eProtein Discovery platform, the User is strongly advised to codon optimize their GOI for expression in E. coli.
Nuclera Technical Support:
UK Phone: +44 1223 942 761
US Phone: +1 508-306-1297
Email: techsupport@nuclera.com
Nuclera Customer Service
UK phone: +44 (0) 1223 974 975
US phone: +1 508-306-1849
email: care@nuclera.com
Offices:
Nuclera UK (HQ):
One Vision Park, Station Road, Cambridge, CB24 9NP, UK
Nuclera USA:
1000 Technology Park Drive, Suite B, Billerica MA 01821, USA
www.nuclera.com
Copyright © 2025 Nuclera Ltd. All trademarks are the property of Nuclera, Ltd. Visit nuclera.com/legal for more info.